| Information supplied by ViaNet |
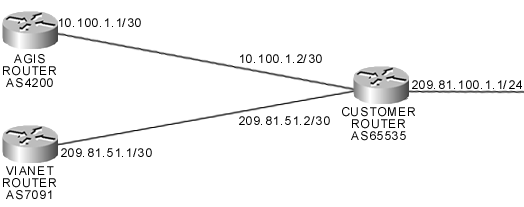
| ViaNet WAN IP address: | 209.81.51.1 |
| Customer WAN IP address: | 209.81.51.2 |
| WAN IP netmask: | 255.255.255.252 |
| LAN IP allocation: | 209.81.100.0/24 |
| LAN IP netmask: | 255.255.255.0 |
| ViaNet ASN: | 7091 |
| AGIS ASN: | 4200 |
| Customer ASN: | 65535 |
! Allow use of zero'th subnet
ip subnet-zero
! Disable obsolete IP address classfulness assumptions
ip classless
interface serial 0/0
desc T1 to ViaNet PacBell Circuit 77HCGF924831-001.pt
ip address 209.81.51.2 255.255.255.252
no shutdown
interface fastether 0/0
desc Local ethernet LAN
ip address 209.81.100.1 255.255.255.0
no ip directed-broadcast
no shutdown
! default route
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial 0/0
router bgp 65535
no synchronization
bgp always-compare-med
bgp log-neighbor-changes
! announcing just 1 /24
network 209.81.100.0 255.255.255.0
neighbor 10.100.1.1 remote-as 4200
neighbor 10.100.1.1 desc AGIS
neighbor 209.81.51.1 remote-as 7091
neighbor 209.81.51.1 desc ViaNet
This config would work, but has some unintended consequences. The main problem
is that BGP's default behavior is to propagate a learned route to each of your
BGP neighbors. The result is that AGIS will see ViaNet routes through you, and ViaNet will see AGIS
routes through you also. You may find youself being flooded by traffic being
routed between AGIS and ViaNet through your router. So, you need a method to allow you to learn routes
from ViaNet and AGIS while only exporting your own routes.
There are several ways to do this, but probably the best way to do this is to use
communities. A community is an arbitrary number (or series of numbers) that you can
associate with an individual route prefix.
Using route-maps, we can tag a route that we learn from a BGP neighbor with a community
(actually, we can tag routes that we learn from any source.) and we can selectively filter out routes
from routing updates that we send to BGP neighbors. These are the two basic properties of
route-maps and communities that we're going to use to control route propogation.
#
# This configuration treats ViaNet as the Primary network feed, and AGIS
# is relegated to being a backup connection.
#
#
ip subnet-zero
ip classless
! Display communities as AS:Number instead of 0XXXXXXXXX
ip bgp-community new-format
interface serial 0/0
desc T1 to ViaNet
ip address 209.81.51.2 255.255.255.252
no shutdown
interface serial 0/1
desc T1 to AGIS
ip address 10.100.1.2 255.255.255.252
no shutdown
interface fastether 0/0
ip address 209.81.100.1 255.255.255.0
no ip directed-broadcast
no shutdown
! Here is where we declare our AS number
autonomous-system 65535
router bgp 7091
no synchronization
bgp always-compare-med
bgp log-neighbor-changes
! Attach a community to local net blocks that we advertise to the outside world
network 209.81.100.0 mask 255.255.255.0 route-map ntwk-to-bgp
! AGIS BGP peering session
neighbor 10.100.1.1 remote-as 4200
neighbor 10.100.1.1 desc AGIS
neighbor 10.100.1.1 version 4
neighbor 10.100.1.1 route-map agis-in in
neighbor 10.100.1.1 route-map agis-out out
! ViaNet Peering Session
neighbor 209.81.51.1 remote-as 7091
neighbor 209.81.51.1 desc ViaNet
neighbor 209.81.51.1 version 4
neighbor 209.81.51.1 route-map vianet-in in
neighbor 209.81.51.1 route-map vianet-out out
! Default route points to ViaNet
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 ser 0/0
! Test to see if we should export a route to an upstream ISP
! We only want to advertise our own statically allocated blocks
ip community-list 1 permit 65535:300
! Attach a community value to statically allocated IP blocks
! (e.g. assigned by upstream ISP or ARIN)
route-map ntwk-to-bgp permit 10
set nlri unicast multicast
set origin igp
set community 65535:300
! Each incoming route prefix from AGIS is run through this route-map.
route-map agis-in 10
set local-preference 100
set community 65535:100
! Each route prefix that we advertise to AGIS is run through
! this route-map. If the match against the 'ip community-list'
! passes, the subsequest route-map statements are executed
! and the route prefix is accepted. Otherwise, the route prefix
! is discarded.
route-map agis-out 10
match community 1
set metric-type internal
! Each incoming route prefix from ViaNet is run through this route-map.
route-map vianet-in 10
set local-preference 200
set community 65535:100
route-map vianet-out 10
match community 1
set metric-type internal
Your CSU/DSU should be set for the following options:
B8ZS/ESF line coding
Clock Source: line
Starting channel: 1
Number of channels: 24
Channel sequence: contiguous
Note: Most brands of CSU/DSU's that we've used (Kentrox/Digital Link/ADTRAN) are
correctly configured for T1 use when reset to factory defaults.
Internet Routing Architectures, Bassam Halabi, Cisco Press/New Riders ISBN 1-56205-652-2
BGP Technical Tips from the Cisco web site
BGP tips from Avi Freedman: 1
2
